Mean squared logarithmic error (MSLE) is a loss function that is used to solve regression problems. MSLE is calculated as the average of the squared differences between the log-transformed actual and predicted values.
The formula to calculate the MSLE:
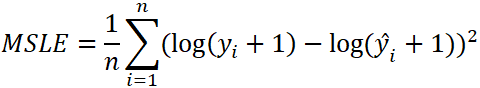
n- the number of data points.y- the actual value of the data point. Also known as true value.ŷ- the predicted value of the data point. This value is returned by model.
Let's say we have the following sets of numbers:
actual values of y | 4 | 0 | 5 | 2 |
predicted values of ŷ | 3.5 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
Here is example how MSLE can be calculated using these numbers:
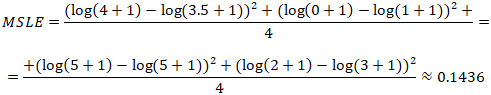
TensorFlow 2 allows to calculate the MSLE. It can be done by using MeanSquaredLogarithmicError class.
from tensorflow import keras
yActual = [4, 0, 5, 2]
yPredicted = [3.5, 1, 5, 3]
msleObject = keras.losses.MeanSquaredLogarithmicError()
msleTensor = msleObject(yActual, yPredicted)
msle = msleTensor.numpy()
print(msle)MSLE also can be calculated by using mean_squared_logarithmic_error, msle or MSLE function.
msleTensor = keras.losses.mean_squared_logarithmic_error(yActual, yPredicted)
msle = msleTensor.numpy()
msleTensor = keras.losses.msle(yActual, yPredicted)
msle = msleTensor.numpy()
msleTensor = keras.losses.MSLE(yActual, yPredicted)
msle = msleTensor.numpy()



Leave a Comment
Cancel reply