Dust is a command line tool for viewing and analyzying disk space usage. This tool can be used as an alternative to the du command.
This tutorial explains how to install Dust on Raspberry Pi.
Install Dust
Use SSH to connect to Raspberry Pi. Retrieve the latest version tag of Dust release from GitHub and assign it to variable.
DUST_VERSION=$(curl -s "https://api.github.com/repos/bootandy/dust/releases/latest" | grep -Po '"tag_name": "v\K[0-9.]+')Next, download tar.gz file from releases page of the Dust repository.
curl -Lo dust.tar.gz "https://github.com/bootandy/dust/releases/latest/download/dust-v${DUST_VERSION}-arm-unknown-linux-gnueabihf.tar.gz"Create temporary directory and extract a tar.gz file:
mkdir dust-temp
tar xf dust.tar.gz --strip-components=1 -C dust-tempRun the following command to move executable file to /usr/local/bin directory:
sudo mv dust-temp/dust /usr/local/binNow dust command will be available for all users as system-wide command.
We can check version of Dust:
dust --versionTemporary directory and tar.gz file are no longer needed, remove them:
rm -rf dust.tar.gz
rm -rf dust-tempTesting Dust
Execute dust command without any arguments to view disk space usage in the current working directory.
dustYou can also view disk space usage of specific directory by providing directory path as argument. For example, /usr/local directory can be analyzed as follows:
sudo dust /usr/local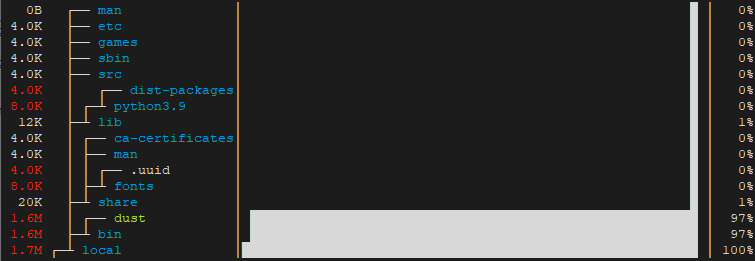
Uninstall Dust
If you decided to completely remove Dust, delete executable file:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/bin/dust



Leave a Comment
Cancel reply