Mean absolute error (MAE) is a loss function that is used to solve regression problems. MAE is calculated as the average of the absolute differences between the actual and predicted values.
The formula to calculate the MAE:
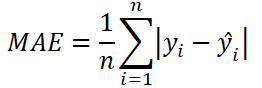
n- the number of data points.y- the actual value of the data point. Also known as true value.ŷ- the predicted value of the data point. This value is returned by model.
Let's say we have the following sets of numbers:
actual values of y | 4 | -1.5 | 5 | 2 |
predicted values of ŷ | 3.5 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
Here is example how MAE can be calculated using these numbers:
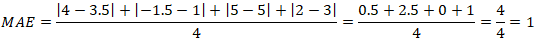
TensorFlow 2 allows to calculate the MAE. It can be done by using MeanAbsoluteError class.
from tensorflow import keras
yActual = [4, -1.5, 5, 2]
yPredicted = [3.5, 1, 5, 3]
maeObject = keras.losses.MeanAbsoluteError()
maeTensor = maeObject(yActual, yPredicted)
mae = maeTensor.numpy()
print(mae)MAE also can be calculated by using mean_absolute_error, mae or MAE function.
maeTensor = keras.losses.mean_absolute_error(yActual, yPredicted)
mae = maeTensor.numpy()
maeTensor = keras.losses.mae(yActual, yPredicted)
mae = maeTensor.numpy()
maeTensor = keras.losses.MAE(yActual, yPredicted)
mae = maeTensor.numpy()



Leave a Comment
Cancel reply