The dive is a command line tool for analyzing a Docker image. This tool shows image contents broken down by layer. It can used to explore image structure in order to minimize size of Docker image.
This tutorial explains how to install dive on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prepare environment
Make sure you have installed Docker in your system. You can read post how to install it.
Install dive
Execute the following command to get the latest version tag of dive release. Assign version tag to variable.
DIVE_VERSION=$(curl -s "https://api.github.com/repos/wagoodman/dive/releases/latest" | grep -Po '"tag_name": "v\K[0-9.]+')Next, download Debian package (.deb) from releases page of the dive repository:
curl -Lo dive.deb "https://github.com/wagoodman/dive/releases/latest/download/dive_${DIVE_VERSION}_linux_amd64.deb"Install dive:
sudo apt install -y ./dive.debOnce installation is completed, we can check dive version:
dive --versionRemove unneeded .deb file:
rm -rf dive.debTesting dive
Run the dive command and provide name of the Docker image as argument. For example, the following command allows to analyze ubuntu image:
dive ubuntu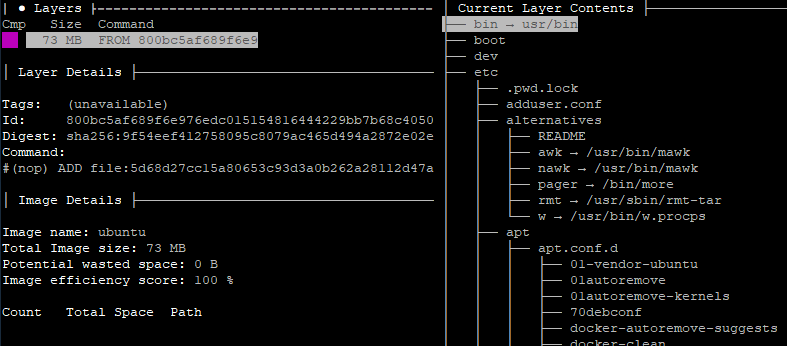
Press CTRL+C, to exit dive.
Uninstall dive
If dive is no longer needed, you can remove it using the following command:
sudo apt purge --autoremove -y dive



Leave a Comment
Cancel reply