The ripgrep is a command line tool which allows searching for strings in files using regex pattern. By default, ripgrep ignores files and directories that specified in .gitignore file. This tool also skips hidden and binary files by default.
This tutorial demonstrates how to install ripgrep on Ubuntu 20.04.
Install ripgrep
Get the latest version tag of ripgrep release and assign it to variable.
RIPGREP_VERSION=$(curl -s "https://api.github.com/repos/BurntSushi/ripgrep/releases/latest" | grep -Po '"tag_name": "\K[0-9.]+')Download Debian package (.deb) from releases page of the ripgrep repository:
wget -qO ripgrep.deb "https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep/releases/latest/download/ripgrep_${RIPGREP_VERSION}-1_amd64.deb"Install ripgrep:
sudo apt install -y ./ripgrep.debWhen installation is finished, we can check ripgrep version:
rg --versionRemove unnecessary .deb file:
rm -rf ripgrep.debTesting ripgrep
Create the following files for testing:
echo "Sample file x1, x2, ..., x10" > test1.txtecho "6x2 + 2x + 1" > test2.txtRun the rg command and provide regex pattern as argument to recursively search for strings in files that are located in the current directory.
rg x[0-9]+
A path to a file or directory can be specified as the second argument.
sudo rg localhost /etc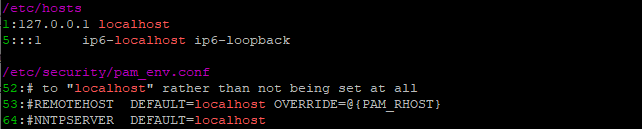
Uninstall ripgrep
If ripgrep is no longer needed, you can remove it using the following command:
sudo apt purge --autoremove -y ripgrep



The 1 Comment Found
Thanks!
Leave a Comment
Cancel reply