Lazydocker is a terminal based UI tool that allows to manage containers, images and volumes for Docker and Docker Compose. Lazydocker is an open-source project written in the Go programming language.
This tutorial shows how to install Lazydocker on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prepare environment
Before starting, make sure you have installed Docker. You can read post how to install it.
Install Lazydocker
Get the latest version tag of Lazydocker release from GitHub. Assign version tag to variable.
LAZYDOCKER_VERSION=$(curl -s "https://api.github.com/repos/jesseduffield/lazydocker/releases/latest" | grep -Po '"tag_name": "v\K[0-9.]+')Download archive from releases page of the Lazydocker repository.
curl -Lo lazydocker.tar.gz "https://github.com/jesseduffield/lazydocker/releases/latest/download/lazydocker_${LAZYDOCKER_VERSION}_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz"Unzip archive:
mkdir lazydocker-temptar xf lazydocker.tar.gz -C lazydocker-tempMove binary file to /usr/local/bin directory:
sudo mv lazydocker-temp/lazydocker /usr/local/binNow lazydocker can be used as a system-wide command for all users.
We can check Lazydocker version:
lazydocker --versionArchive and temporary directory is no longer necessary, remove them:
rm -rf lazydocker.tar.gz lazydocker-tempTesting Lazydocker
Run hello-world image inside a container:
docker run hello-worldStart Lazydocker:
lazydockerYou will see all of your images, containers, and volumes.
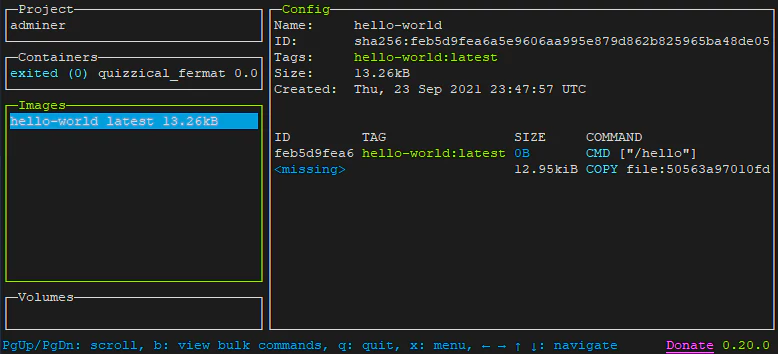
Press CTRL+C, to exit Lazydocker.
Uninstall Lazydocker
If you decided to completely remove Lazydocker, delete the binary file:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/bin/lazydockerYou can also remove Lazydocker config directory:
rm -rf ~/.config/lazydocker



Leave a Comment
Cancel reply